
Follow that line until reaching a temperature of 100F. What is the enthalpy value of the gas?įrom the carbon dioxide diagram, Figure A-4 of Appendix A, locate the pressure of 100 psia. The intersection of the two lines gives anenthalpy that is equal to h = 115 Btu/lbm.Ĭarbon dioxide is used in a particular process in which the pressure is 100 psia and the temperatureis 100F. Follow that line until reaching a quality of 70%. What is the enthalpy of the mercury if its pressure is100 psia and its quality is 70%?įrom the mercury diagram, Figure A-3 of Appendix A, locate the pressure of 100 psia. The use of such diagrams is demonstrated by the followingtwo examples.Įxample 3: Use of the h-s diagram Mercury is used in a nuclear facility. "state" of the substance is usually obtained through the use of T-s (temperature-entropy) and h-s (enthalpy-entropy) diagrams, available in most thermodynamics texts for common substances.
Locate point 1 at theintersection of the 700 psia and the 680Fįollow the entropy line downward verticallyto the 140 psia line and read h = 1178 Superheated steam at 700 psia and 680F is expanded at constant entropyto 140 psia.
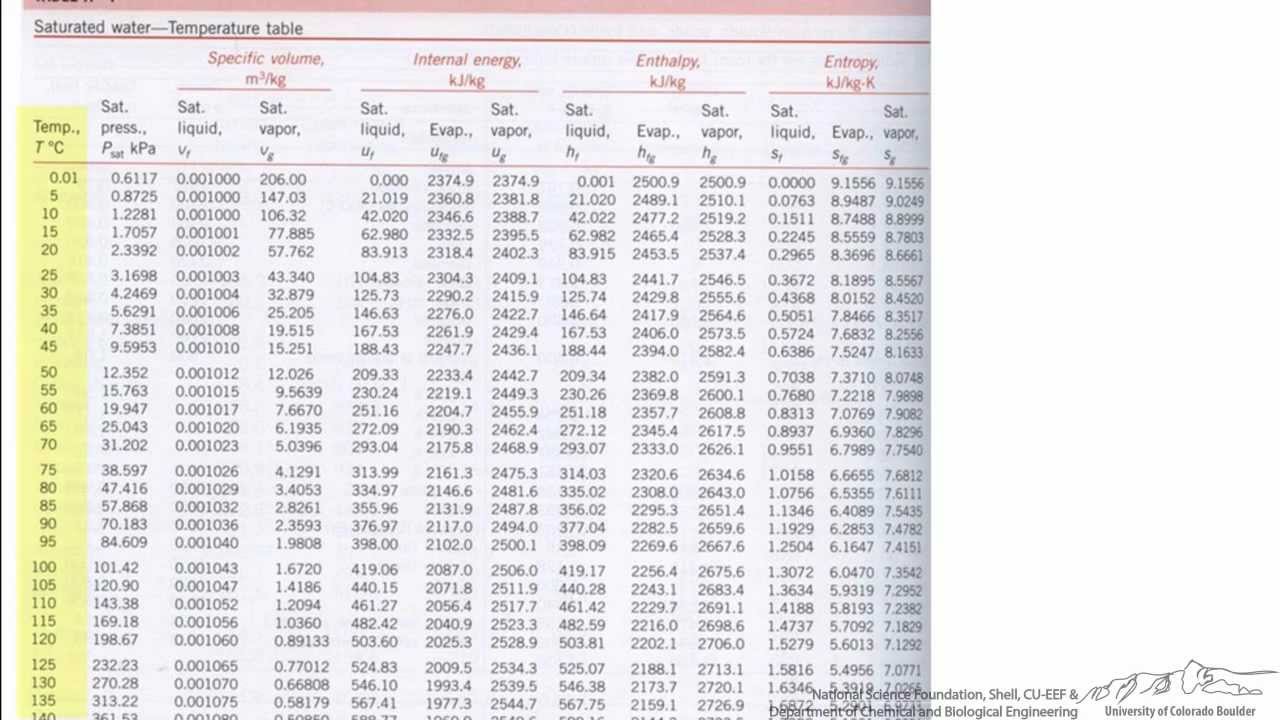
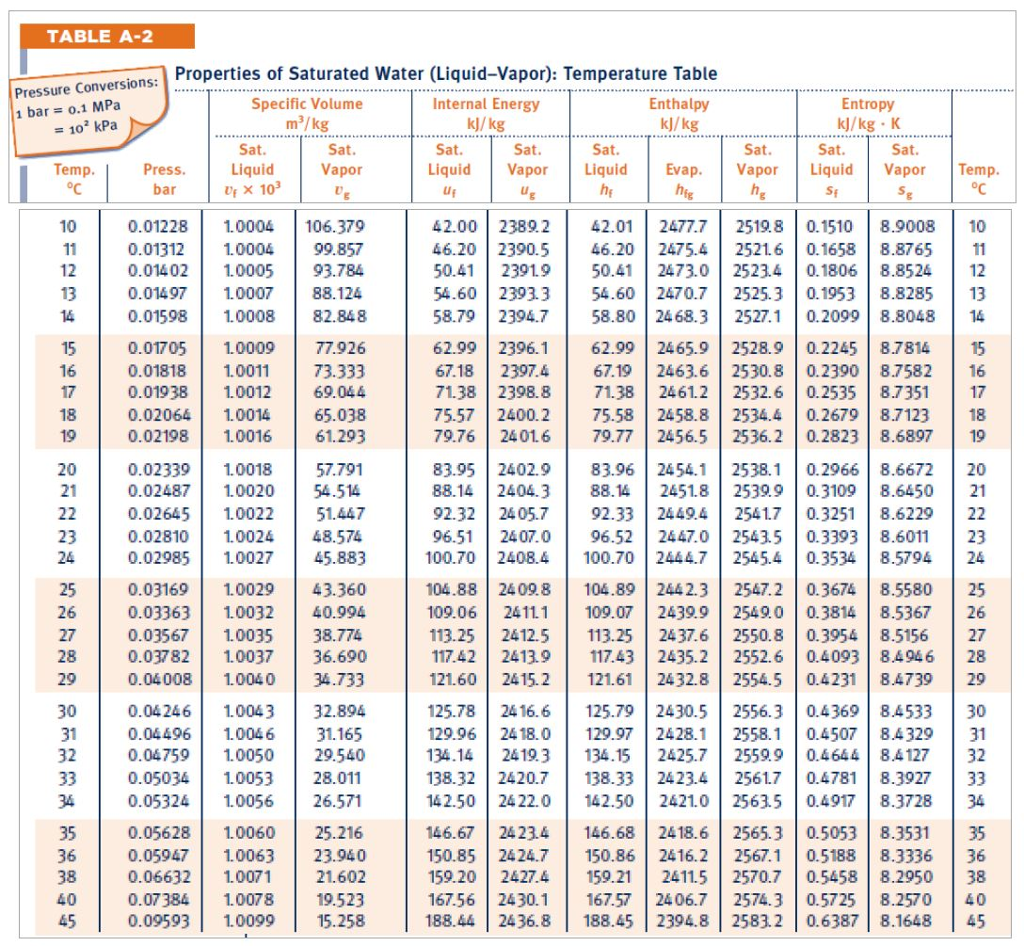
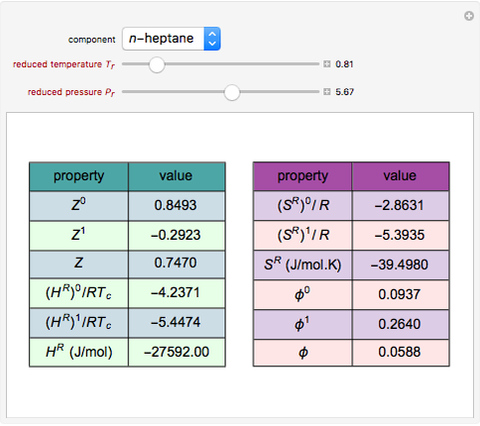
The following two examples illustrate the useof the Mollier diagram and the steam tables.Įxample 1: Use of Mollier Chart. These other properties are usually obtained utilizingeither the Mollier diagram (if the substance is steam) or the saturated and superheated steam tables,as shown in the Figures A-1 and A-2. Usually,two properties (for example, v, p, T, h, s) of the substance must be known in order to determinethe other needed properties. In order to solve problems in Thermodynamics,information concerning the "state" of the substance studied must be obtained. These relationships are used with the saturated steam tables. The following relationships exist between the quality of a liquid-vapor mixture and the specific volumes, enthalpies, or entropies of both phases and of the mixture itself. The key property of such mixtures is steam quality (x), defined as the mass of steam present per unit mass of steam-water mixture, or steam moisture content (y), defined as the mass of water present per unit mass of steam-water mixture. Most practical applications using the saturated steam tables involve steam-water mixtures. Hence, the enthalpy (hf) of saturated liquid and the entropy (sf) of saturated liquid have values of approximately zero at 32F. The values of enthalpy and entropy given in these tables are measured relative to the properties of saturated liquid at 32F. Figure A-2 shows a portion of a typical saturated steam temperature table and a portion of a typical saturated steam pressure table. Normally, the saturated steam tables are divided into two parts: temperature tables, which list the properties according to saturation temperature (Tsat) and pressure tables, which list them according to saturation pressure (Psat). The saturated steam tables give the energy transfer properties of saturated water and saturated steam for temperatures from 32 to 705.47F (the critical temperature) and for the corresponding pressure from 0.08849 to 3208.2 psi. Some tables use v for n (specific volume) because there is little possibility of confusing it with velocity. The following notation is used in steam tables. Both sets of tables are tabulations of pressure (P), temperature (T), specific volume (n), specific enthalpy (h), and specific entropy (s).
Portions of the tables are shown in Figure A-2. Steam tables consist of two sets of tables of the energy transfer properties of water and steam saturated steam tables and superheated steam tables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
